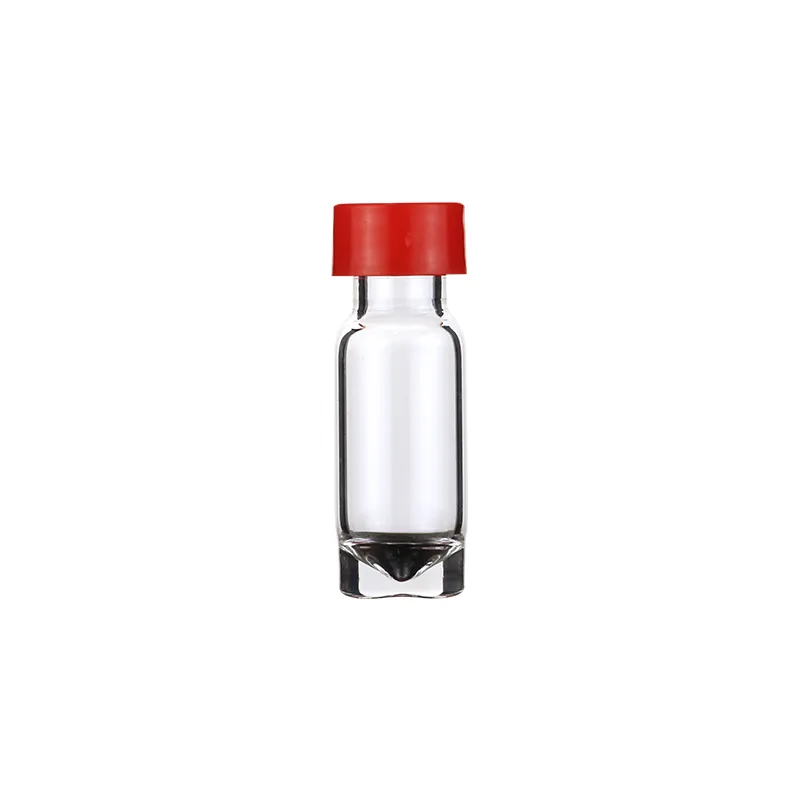
Demystifying V-Vials: Nanoscale Packaging Technology
Introduction
In modern biomedical and material science, how to effectively encapsulate and stably store active substances has always been a central challenge. However, traditional encapsulation methods are often difficult to balance stability, targeting and bioavailability, which restricts the application and promotion of many innovative therapies.
Although encapsulation technologies such as liposomes and polymer microspheres have made significant progress in the field of drug delivery, they still face key challenges such as defective thermal stability, insufficient precision of targeted release, and ceiling of bioavailability.
In the face of these bottlenecks, a brand new encapsulation container, v-vials, has emerged. How does it break through the limitations of traditional encapsulation containers? In this article, we will discuss the scientific principles, technical advantages, and prospects for widespread application of v-vials.
Technology Deconstruction
The creation of v-vials marks a new era of nanoscale engineering in packaging technology. With breakthrough innovations in materials science and cutting-edge nano-fabrication processes, the technology achieves disruptive improvements in stability, precise controlled release and bioavailability.
1. Material breakthrough: supramolecular silicone-based compliant materials and surface functionalization
Through molecular self-assembly technology, v-vials uses supramolecular organosilicon based composites to achieve nanoscale stable encapsulation. Its high heat resistance and mechanical strength enable it to remain stable in extreme environments, avoiding the easy degradation problems of traditional liposomes and polymer microspheres.
The advanced anti-protein adsorption coating significantly reduces non-specific protein adsorption and immune system recognition, thus enhancing the circulating half-life of the drug and improving the efficiency of targeted delivery.
2. A leap in performance: pushing the limits of traditional packaging technology
98.7% active ingredient preservation rate (-80℃ to 60℃ extreme test)
-
- V-vials can still maintain the high efficiency and stability of active ingredients under extreme temperature environment, far exceeding the preservation ability of traditional encapsulation materials, providing a revolutionary solution for vaccines, enzymes and gene therapy vectors.
Precise controlled release at 0.5nm level (animal experimental data for liver cancer targeted drugs)
-
- Through nanoscale pore size regulation, v-vials can realize high-precision slow release, ensuring the precise release of anti-cancer drugs at the target site, significantly reducing systemic toxicity and improving therapeutic efficacy.
V-vials’ nanoscale engineering technology not only solves the core bottleneck of traditional encapsulation technology, but also provides a revolutionary solution for next-generation precision medicine, gene therapy and targeted drug development.
Application Scenario Re-engineering
V-vials’ breakthrough nanoscale packaging technology has not only demonstrated outstanding performance benefits in the lab, but has also made the leap from proof-of-concept to real-world applications in multiple industries. From biomedicine to food industry to environmental science, V-vials are reshaping the technology landscape in many fields.
1. Biomedicine: a revolutionary breakthrough in precision delivery and stability
Vaccine Revolution: Vaccine Ambient Storage Feasibility Validation
-
- V-vials brings new opportunities for vaccine popularization in developing countries through its ultra-high stability encapsulation technology, which enables vaccines to maintain their effectiveness at 25°C, dramatically reducing the cost of cold chain transportation.
Gene Therapy: 300% Increase in CRISPR Vector Delivery Efficiency
-
- CRISPR vectors encapsulated with v-vials have demonstrated a 3-fold increase in delivery efficiency in cellular experiments, improving the success rate of gene editing. It also significantly reduces off-target effects.
New paradigm in anti-cancer: synergistic release of PD-1 inhibitors + chemotherapeutic agents
-
- Through nanoscale controlled release technology, v-vials can realize the precise proportional release of PD-1 inhibitors and chemotherapeutic drugs, improving efficiency and reducing side effects.
2. Disruption in the food industry: dual upgrading of taste and nutrition
Molecular Encapsulation of Flavor
-
- With v-vials nano encapsulation technology, the flavor molecules can be protected during cooking or storage, and released at oral temperature to achieve a longer lasting and more natural flavor experience.
Breakthrough in probiotic survival rate from 15% to 89%.
-
- While traditional probiotics have a low survival rate from the digestive tract, v-vials dramatically enhance their functionality by increasing the survival rate of probiotics in the stomach acid environment to 89% through nanoscale protective layer technology.
3. Environmental science applications: precision mitigation and sustainable development
Microbial Remediation Agents for Precision Slow Release
-
- In some of the remediation experiments, microbial remediators encapsulated with v-vials have improved the efficiency of delivery by 60% compared to traditional methods, and realized long-lasting slow release.
Pesticide see 50% of the field trial data
-
- With v-vials carrier technology, the target delivery efficiency of pesticides is dramatically improved, reducing pesticide use by 50% while maintaining control effects, contributing to the sustainable development of agriculture.
The industrialization of V-vials is accelerating, which not only solves the pain points of traditional encapsulation technology, but also brings unprecedented changes in several industries. In the next section, we will explore the future direction of the technology and its long-term impact on the industry.
New Challenges
V-vials, a revolutionary breakthrough in nanoscale encapsulation technology, have raised a number of issues while advancing biomedicine, the food industry and environmental science. From biosafety to adjustments in global regulatory frameworks, the widespread use of v-vials requires more rigorous scientific validation and policy support to ensure their safety and sustainability.
1. The biosafety controversy: unresolved metabolic and ecological risks
Uncertainty in the in vivo metabolic pathways of nanoparticles
-
- Due to the high surface area and unique physicochemical properties of nanomaterials, the metabolic pathways of v-vials in living organisms still have unknown variables.
Lag in ecotoxicity assessment
-
- Certain nanoparticles may pose potential hazards to the ecosystem.
2. Reconfiguring regulatory frameworks: policy adaptation to nanotechnology
Changes in the road to FDA approval of novel delivery systems
-
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is currently restructuring its approval process for novel nanodelivery systems to require more advanced biodistribution, degradation kinetics, and long-term safety data. This means that v-vials will need to go through a more rigorous clinical evaluation cycle for medical applications such as drug delivery.
ISO/TC229 nanotechnology standards update process
-
- The TC229 Nanotechnology Committee under the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is advancing the updating of global nanotechnology standards covering nanomaterial characterization, safety assessment and environmental sound control. This will have a direct impact on the compliance requirements for v-vials in the global market, design and production, labeling, risk assessment and environmental impact management.
Looking ahead: balancing innovation and security for the future
As a cutting-edge innovation in nanoscale encapsulation technology, V-vials need to actively respond to biosafety and ethical challenges while promoting industrial applications. In the future, technology research and development and policy regulation need to be promoted simultaneously to ensure that v-vials are industrialized and landed within a controllable and safe framework through scientific research, industry standards and global collaboration.
Conclusion
The breakthrough of V-vials is not only a cool change in encapsulation technology, but also a qualitative change in the way matter is manipulated. It not only enhances the preservation ability of matter, but also gives it programmable behavioral modes, which is the shift of encapsulation technology from passive protection to active regulation, thus triggering profound philosophical and social changes.
The industrialization of V-vials technology will greatly contribute to the decentralization of the pharmaceutical and food supply chain; and the popularization of precision drug delivery technology will improve the accessibility of personalized medicine and provide more efficient and affordable treatments to countries of different economic levels.
Against the backdrop of global health standards, the breakthrough of v-vials is not only about technological innovation, but also an opportunity to democratize science and technology, so that advanced encapsulation technology is no longer the exclusive property of a few countries and companies, but can be widely applied globally to promote the sustainable development of healthcare, food and environmental sciences.
V-vials represents not only the progress of an industry, but also a new era of packaging technology towards intelligence and autonomy. From preservation to programming, from physical barriers to precise control, v-vials are redefining the way humans interact with the material world. In the future, with the further integration of nanotechnology and artificial intelligence, the encapsulation technology may no longer be a container for Bejing, but become an “intelligent carrier” in the true sense of the word, and promote the global scientific and technological civilization to a new dimension.
 Italiano
Italiano Português
Português
