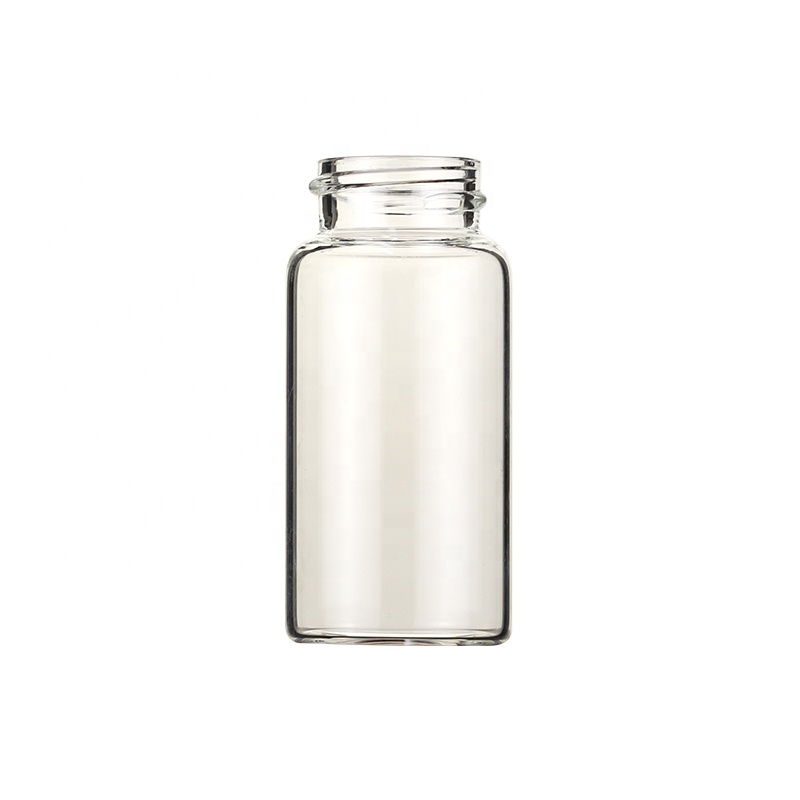
How to Choose the Right Scintillation Vials?
🔥 Introduction
Scintillation vials are an integral part of liquid scintillation counting experiments and serve to contain the sample and scintillation fluid and detect the decay of radioisotopes through efficient photon transmission. Choosing the right scintillation vials has a direct impact not only on the accuracy and reliability of the results, but also on the cost-effectiveness and ease of operation.
This paper aims to provide researchers with a comprehensive guide to selecting the most appropriate type and size of scintillation vials based on sample characteristics, experimental conditions, and instrumentation requirements, in order to optimize experimental performance and ensure data accuracy and reproducibility.
🔥 Types of Scintillation Vials
The types of scintillation vials are mainly categorized into glass bottles, plastic bottles drinking special material bottles, each type has its unique advantages, disadvantages and applicable scenarios.
Glass scintillation vials
Low cost: Glass bottles are usually less expensive and are suitable for experiments with limited budgets.
Chemically inert: glass shows good inertness to most chemicals and does not react easily with samples.
High transparency: glass vials have excellent optical transparency, which contributes to the efficiency of photon transmission.
Fragile: glass vials are prone to breakage and require extra care when handling.
Higher background counts: Naturally occurring radioactive elements in glass may result in higher background counts.
-
- Applications: Suitable for routine liquid scintillation counting experiments, especially in cost-sensitive scenarios where very low background counts are not required.
Plastic scintillation vials
Unbreakable: Plastic bottles are resistant to drops and impacts, making them safer to handle.
Low background count: Plastic materials usually do not contain natural radioactive elements and are suitable for low background count experiments.
Recyclable: Some plastic bottles can be reused or recycled, which is more environmentally friendly.
Possible chemical adsorption: Some plastic materials may adsorb chemicals in the samples, which may affect the experimental results.
-
- Applications: Suitable for low background counting experiments (e.g., environmental sample testing) as well as scenarios that require a high degree of safety and durability.
Specialized scintillation vials
Low Potassium Glass Bottle
-
- Features: Significantly reduces background counts by reducing the potassium content of the glass.
- Application: For high sensitivity experiments requiring low background counts.
Polytetrafluoroethylene bottles
-
- Characteristics: Excellent chemical resistance, suitable for samples with strong acids, bases or organic solvents.
- Application: suitable for corrosive samples or experiments in special chemical environments.
Micro scintillation vials
-
- Features: small size, suitable for experiments with limited sample volume.
- Application: suitable for micro sample detection or high throughput screening experiments.
By understanding the characteristics of different types of scintillation vials, researchers can choose the most suitable type according to their experimental needs, thus optimizing the results and improving the efficiency of their experiments.
🔥 Dimensions of Scintillation Vials
The size of the scintillation vials is a critical factor in the experimental design and directly affects sample handling, counting efficiency, and accuracy of experimental results.
Common sizes
Common sizes of scintillation vials include
-
- 7ml: medium size, suitable for most routine liquid scintillation counting experiments.
- 20ml: suitable for large samples or experiments requiring high sensitivity detection.
Selection factors
When selecting a scintillation vial size, consider the following factors:
-
- Sample volume: Ensure that the scintillation vials can accommodate the sample volume while leaving enough room to add scintillation liquid.
- Volume of scintillation solution: The ratio of scintillation solution to sample is critical to counting efficiency and should be adjusted according to experimental requirements.
- Instrument compatibility: Different liquid scintillation counters have specific requirements for scintillation vials sizes, so make sure that the chosen size is compatible with the instrument.
The importance of choosing the right size
-
- Maximize counting efficiency: The right size ensures that the sample is in full contact with the scintillation fluid, thus increasing the photon collection efficiency. A bottle that is too large may dilute the sample and reduce the efficiency of the technique, while a bottle that is too small may limit the sample volume and affect the sensitivity of the assay.
- Minimize background counts: Selecting the right size can reduce unnecessary scintillation fluid usage, thus lowering background counts.
- Avoid spills or leaks: Proper sizing prevents spillage of samples or scintillation fluids, ensuring safe and clean experimental operations.
Practical application recommendations
-
- Micro samples: Choose miniature scintillation vials to ensure efficient mixing of the sample with the scintillation solution.
- Routine experiments: 7ml scintillation vials are ideal for most experiments, balancing sample volume and counting efficiency.
- Large volume samples: 20ml scintillation vials are suitable for experiments requiring high sensitivity or large sample volumes, such as environmental monitoring or biological sample analysis.
By choosing the right scintillation vials, researchers can optimize experimental conditions, improve data quality, and ensure the efficiency and safety of the experimental process.
🔥 Other Considerations
In addition to the type and size of the right scintillation vials, there are a number of other key factors that need to be carefully considered to ensure the success of the experiment and the accuracy of the data.
Cap type
Importance: The sealing of the cap directly affects the reliability of the experimental results and the safety of the operation.
-
- Screw cap: Provides a good seal to prevent leakage and evaporation, suitable for long term storage or volatile samples.
- Pressure cap: Easy to handle and suitable for quick sealing, but sealing may be slightly less than screw cap.
- Internal gasket design: Some caps have an internal gasket (e.g. PTFE or silicone) to further improve sealing and prevent chemisorption.
Selection advice: Depending on the volatility of the sample and the experimental period, choose the right type of cap to ensure a tight seal and ease of handling.
Bottle design
Importance: Bottle mouth design affects ease of filling, clarity and handling.
-
- Wide-mouth bottles: easy to fill and clean, suitable for viscous samples or experiments that require frequent handling.
- Narrow-mouth bottles: reduce sample exposure and are suitable for volatile or air-sensitive samples.
Selection advice: Choose the appropriate bottle mouth design according to the sample characteristics and experimental operation needs to improve the experimental efficiency.
Transparency
Importance: The transparency of scintillation vials directly affects the photon transmission efficiency, and thus the counting efficiency and experimental sensitivity.
Glass vials usually have a high degree of transparency, but it is important to note the effect of glass type (e.g. low potassium glass) on transparency.
The transparency of plastic vials varies depending on the material, and optically superior materials (e.g., polystyrene) should be selected.
Selection advice: Ensure that scintillation vials have high transparency in the detection wavelength range to maximize photon collection efficiency.
Chemical compatibility
Importance: The right scintillation vials material must be compatible with the cartridge scintillation solution to avoid chemical reactions or adsorption that could affect experimental results.
Plastic vials may adsorb certain organic compounds, resulting in sample loss or contamination.
Glass vials may be corroded by strong alkalis, affecting their performance.
Suggestion for selection: For corrosive samples (e.g., strong acids and bases), select a chemically resistant material (e.g., PTFE bottle). For organic solvents or special chemicals, test the compatibility of bottle materials to avoid adsorption or reaction.
Other Precautions
-
- Cleaning and Reuse: Some scintillation vials are reusable, make sure they are easy to clean and do not affect the results of subsequent experiments.
- Labeling and marking: Choose a bottle material that is suitable for labeling and easy sample identification and tracking.
- Balancing cost and performance: Choose the type and size of scintillation vials that offer the best value for money while meeting your experimental needs.
By taking the above factors into consideration, researchers can further optimize the selection of scintillation vials to ensure the efficiency, safety and data reliability of their experiments.
🔥 Conclusion
The choice of scintillation vials, a key component in liquid scintillation counting experiments, plays a decisive role in the success of the experiment. Whether it is the type and size of the scintillation vials, or the cap design, transparency or chemical compatibility, every detail may affect the accuracy, reliability and reproducibility of the experimental results.
Choosing the right scintillation vials is critical to the success of an experiment, and optimizing the choice of scintillation vials improves data quality, reduces costs, and improves experimental efficiency by taking into account the sample type, experimental requirements, and instrumentation specifications based on the chemical nature of the sample.
In conclusion, the selection of scintillation vials is not just a detail in the experimental design, but one of the key factors determining the success of an experiment. By comprehensively considering the sample characteristics, experimental requirements and instrument specifications, researchers can make the best choice to ensure the efficiency, economy and data card blooding of the experiment.
 Italiano
Italiano Português
Português
